In today’s fast-paced world, agriculture is not exempt from the rapid advancements in technology. One such innovation that has revolutionized the farming industry is the utilization of big data. Big data in agriculture has become a game-changer, enhancing crop yield and farming efficiency in unprecedented ways. This article explores the impact of big data on agriculture, from precision farming to predictive analytics, and sheds light on how it is shaping the future of farming.
Introduction
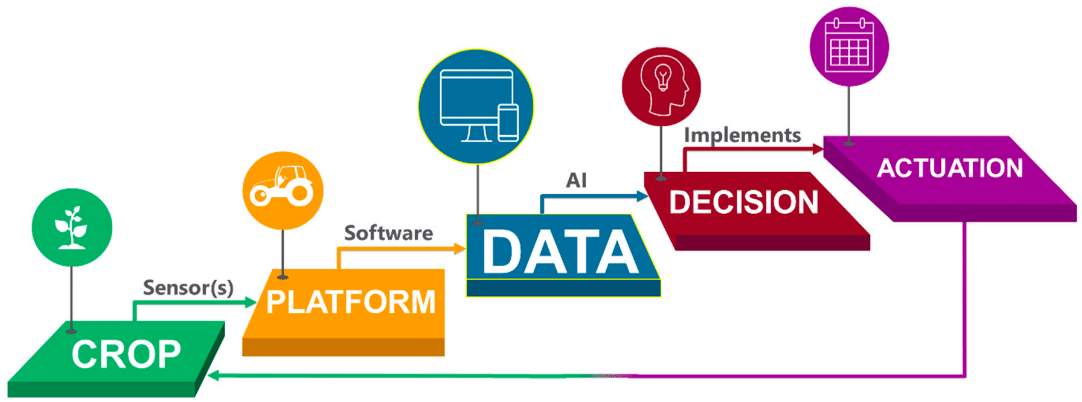
Traditional farming methods, while effective in their own right, often lack the precision and efficiency demanded by a growing global population. Big data, a term referring to the massive volumes of structured and unstructured data that can be analyzed to extract valuable insights, has found its way into the world of agriculture. This integration is changing the way farmers approach their craft.
The Power of Data
The power of data is undeniable in today’s digital age. Data has transformed the way we live, work, and make decisions across various fields, from business and healthcare to education and government. Its impact is far-reaching and continues to grow as technology advances. Here are some key aspects of the power of data:
- Informed Decision-Making: Data provides valuable insights that enable individuals and organizations to make informed decisions. Whether it’s a business optimizing its operations or a doctor diagnosing a patient, data-driven decisions lead to better outcomes.
- Improved Efficiency: Data helps streamline processes and operations. By analyzing data, organizations can identify bottlenecks, reduce waste, and increase efficiency in various aspects of their work.
- Personalization: Data allows for personalization on a large scale. Companies use customer data to tailor their products and services, enhancing the customer experience. This personal touch can lead to increased customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Predictive Analytics: With the power of data, predictive analytics has become a reality. By analyzing historical data, trends, and patterns, organizations can make forecasts and predictions about future events and trends, helping them prepare for various scenarios.
- Scientific Discoveries: In fields like astronomy, genomics, and climate science, data plays a pivotal role in making groundbreaking discoveries. Massive datasets are analyzed to uncover hidden patterns, contributing to our understanding of the universe and the natural world.
- Healthcare Advancements: Patient data, combined with machine learning and AI, is revolutionizing healthcare. It allows for more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and early detection of diseases.
- Social Impact: Data can be a powerful tool for addressing social issues. Governments and organizations can use data to identify areas of need, allocate resources efficiently, and measure the impact of social programs.
- Business Competitiveness: In the business world, data-driven companies have a competitive advantage. They can adapt quickly to market changes, identify emerging trends, and make strategic decisions based on data.
- Smart Cities: Data is at the heart of the concept of smart cities. Through sensors and data analysis, cities can optimize traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and enhance overall quality of life for residents.
- Ethical Considerations: With great power comes great responsibility. The collection and use of data raise ethical concerns about privacy, security, and the potential for bias in algorithms. It’s crucial to address these issues to harness the power of data responsibly.
In conclusion, the power of data is transformative and touches nearly every aspect of our lives. As we continue to generate and analyze more data, it’s essential to use it wisely and ethically to unlock its full potential for the benefit of individuals, organizations, and society as a whole.
Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture is one of the most significant beneficiaries of big data. By utilizing data-driven insights, farmers can optimize the use of resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides. This not only reduces waste but also leads to higher crop yields.
Weather Forecasting and Data
Weather plays a crucial role in farming success. Big data enables farmers to access real-time weather data and forecasts. By understanding weather patterns, farmers can make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and irrigation.
Soil Health Analysis
Understanding the health of the soil is vital for sustainable farming. Big data allows for continuous monitoring of soil conditions, helping farmers identify nutrient deficiencies and adjust their soil management practices accordingly.
Crop Monitoring with Drones
Drones equipped with advanced sensors and cameras are becoming a common sight on farms. These drones provide high-resolution images of crops, helping farmers detect issues such as pest infestations and nutrient deficiencies early.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast future events. In agriculture, this can help farmers predict crop yields, identify potential disease outbreaks, and optimize planting schedules.
Pest and Disease Management
Big data aids in the early detection of pests and diseases. By closely monitoring data on crop health and environmental conditions, farmers can take proactive measures to prevent or mitigate infestations.
Resource Optimization
Resource optimization is a key advantage of big data in agriculture. Farmers can precisely allocate resources like water and energy, reducing waste and environmental impact.
Market Insights
Access to market data empowers farmers to make informed decisions about crop selection and pricing strategies. Big data helps farmers align their production with market demand.
Challenges Faced
While big data offers immense benefits, it also presents challenges such as data security and the need for advanced technology adoption. These challenges must be addressed for sustainable implementation.
Future Prospects
The future of big data in agriculture looks promising. As technology continues to advance, farmers can expect even more sophisticated tools and data-driven solutions to enhance their productivity and sustainability.
Conclusion
Big data has ushered in a new era of farming, where data-driven decisions are the norm. From precision agriculture to predictive analytics, the benefits are undeniable. As we move forward, it is imperative that farmers embrace this technological revolution to secure a sustainable future for agriculture.